Short Disclaimer: This post may contain affiliate links at no extra cost to you. Visit our Disclaimer Page for more details.
In a word, what is merchandising? It is a process whose main objective is to determine the process and channel of product sales to the customer at the right price and maintain the profitability for the Organization.
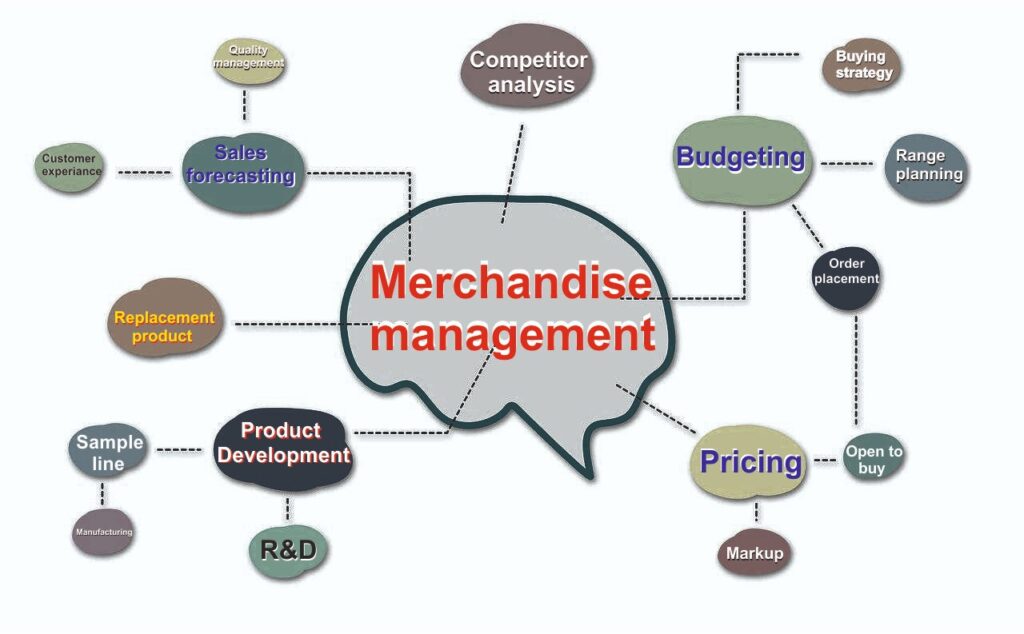
Through that process, product sales and profit maximization are determined through specific methods, Such as Product identification, product pricing, promotion, inventory management, and presentation of the right product at the right time.
Effective merchandising increases the propensity to buy products among consumers in the market by understanding the competitive landscape and increasing the experience of impulse buying among customers.
What Is Merchandising? Discover the Proven Strategy That Sells
1. Visual Merchandising:
It involves presenting products in a visually appealing manner to attract customers and encourage sales. This includes window display, store layout, product placement, signage, and website display.
2. Online Merchandising:
In the digital world, merchandising plays a role in getting customers interested in online shopping through various methods, such as website layout, accurate product descriptions, images, and videos and mainly selling products by turning the customer’s digital journey into a real journey.
3. Seasonal Merchandising:
Usually, retailers offer different offers during different auctions or festivals. Merchandiser helps to capitalize on customer behavior at this time or auction.
4. Offline-Store Merchandising:
This refers to the arrangement and display of products within a physical retail store. It includes shelf displays, end caps, product demonstrations, and interactive displays.
5. Promotional Merchandising:
This involves promotional tactics such as discounts, coupons, buy-one-get-one (BOGO) offers, and limited-time promotions to stimulate sales and attract customers.

6. Cross-Merchandising:
Cross-merchandising is a process of displaying similar types of products to encourage additional purchases. For example, displaying chips and salsa together or suggesting a matching tie with a shirt.
7. Experiential Merchandising:
This involves creating immersive and interactive experiences for customers to engage with products. Examples include pop-up shops, interactive displays, and product demonstrations.
8. Product Merchandising:
This involves selecting and sourcing products, determining pricing strategies, and managing inventory to meet customer demand and achieve sales targets.
9. Impulse Merchandising:
This strategy involves placing low-cost, high-margin items strategically near checkout counters or other high-traffic areas to encourage the customer at last-minute purchases.
10. Regional Merchandising:
In this manner, regional traffic is usually enticed with their preferred product, which helps to increase the year’s overall sales and turnover.
For example, products that customers like in South India may not like in North India So following these likes and dislikes metrics, products are promoted online and in retail stores through displays or catalogs.
These are just a few examples of the different types of merchandising strategies employed by retailers and online to drive sales and enhance the shopping experience for customers.
From Shelf to Cart: 7 Proven Products Merchandising Tactics
Product merchandising serves several important purposes for business. This process helps the business to weigh its pros and cons before making any decision.
It is the job of the merchandising department to research and determine how much prominence a product can create in the market.
Several specific strategies specifically address this process.

1. Increase Sales:
Effective merchandising strategies can help attract customers, drive traffic to stores, and ultimately increase sales. By presenting products appealingly and enticingly, businesses can encourage impulse purchases and maximize the chances of customers making a purchase.
2. Enhance Brand Image:
Merchandising plays a crucial role in shaping the perception of a brand. A well-executed merchandising strategy can convey the brand’s values, identity, and quality standards. Consistent branding across all merchandising efforts helps reinforce brand image and build customer loyalty.
3. Improve Customer Experience:
A carefully curated and organized retail environment can enhance the overall shopping experience for customers. By making it easy for customers to find what they need and discover new products, businesses can foster positive interactions and increase customer satisfaction.
4. Optimize Inventory Management:
Merchandising involves strategic planning and management of inventory to ensure that products are available when and where customers need them.
By analyzing sales data and customer trends, businesses can make informed decisions about product assortment, pricing, and replenishment to minimize stockouts and reduce excess inventory.
5. Differentiate from Competitors:
In a crowded marketplace, effective merchandising can help businesses stand out from competitors and attract attention. By offering unique product displays, promotions, and experiences, businesses can create a distinct identity and capture the interest of potential customers.
6. Drive Brand Loyalty:
Consistent and engaging merchandising efforts can foster a sense of loyalty and connection with customers.
By providing memorable shopping experiences and delivering on promises, businesses can build long-term relationships with customers who are more likely to return and recommend the brand to others.
7. Maximize Profitability:
Merchandising is closely tied to revenue generation and profitability. By optimizing product placement, pricing strategies, and promotions, businesses can maximize the return on investment and achieve higher margins.
Overall, merchandising is essential for businesses to effectively showcase their products, attract customers, and drive sales.
It involves a combination of strategic planning, creativity, and attention to detail to create compelling shopping experiences that resonate with customers and drive business success.
Discover the 4 Essential Differences Between Merchandising and Product Management.
While there may be overlap in some areas, such as product assortment planning and pricing optimization, merchandising and product management are distinct functions with their specific objectives, focus areas, and responsibilities within a business.
Both are critical for the success of retail and consumer goods companies, but they address different aspects of the product lifecycle and customer experience.
1 Focus:
•Merchandising: Primarily focuses on the presentation, promotion, and sale of products to customers. It involves activities such as product display, assortment planning, pricing, and promotion strategies aimed at driving sales and maximizing profitability.
•Product Management: Primarily focuses on the lifecycle of a product from ideation to development, launch, and ongoing management. Product managers are responsible for defining product features, prioritizing enhancements, and ensuring that the product meets customer needs and business objectives.
2. Scope:
•Merchandising: Typically involves managing existing product assortments within a retail environment. Merchandisers analyze sales data, customer trends, and market dynamics to make decisions about product selection, pricing, and presentation.
•Product Management: Involves overseeing the entire lifecycle of a product, including market research, competitive analysis, product development, launch planning, and post-launch optimization.
Product managers work closely with cross-functional teams such as engineering, marketing, and sales to bring products to market and drive their success.
3. Timeframe:
•Merchandising: Often focused on short-term goals and objectives related to sales performance and inventory management. Merchandisers may adjust product assortments, pricing, and promotions frequently based on seasonal trends, customer demand, and market conditions.
•Product Management: Typically involves longer-term planning and strategic decision-making aimed at achieving product roadmap objectives and business goals. Product managers may prioritize features and enhancements based on market research, customer feedback, and strategic direction, considering both short-term and long-term impacts.
4. Responsibilities:
•Merchandising: Responsibilities include product assortment planning, inventory management, pricing optimization, promotional planning, and visual merchandising.
•Product Management: Responsibilities include defining product vision and strategy, gathering and prioritizing requirements, collaborating with cross-functional teams, managing product development processes, and analyzing product performance metrics.
Conclusion:-
Product merchandising serves several important purposes for business. So we can easily know what merchandising is through this article. Merchandising is an important process. Which makes a special contribution to the progress of